DSA Technologies works with a wide range of businesses, that face many of the same security challenges over and over. Most of these issues are preventable or can at least be mitigated with the right care and awareness. Here’s what the resident expert Michael Reese at DSA Technologies shared with being the most common problems that you should keep an eye out for.
- Phishing Schemes
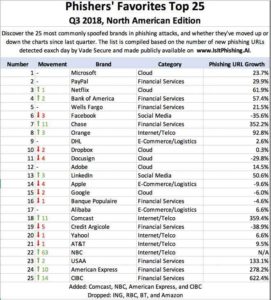
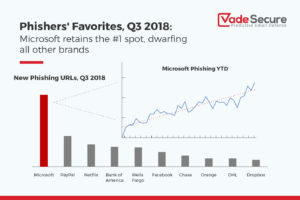
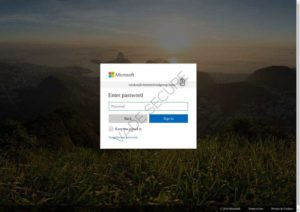
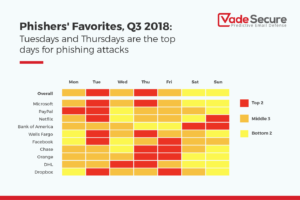
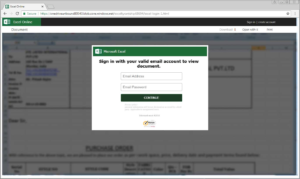
Phishing is the crime of deceiving people into sharing sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers. Nearly all successful cyber-attacks begin with a phishing scheme. These attacks are responsible for over $12 billion losses globally! Usually the attack is delivered in the form of an email and will demand that the victim go to a website and take immediate action. If the user clicks the link, they are sent to a fake website that imitates a real website. From here, they are asked to login. The criminal now has your information to cause more damage. - Cloud Cyber Security Threats
Cloud computing, or the use of an internet source to store information, has grown significantly. Most people assume that cloud storage is safe, but this isn’t necessarily the case. If your provider offers minimal security your sensitive data could be easily accessible to hackers. The amount of security your cloud server offers is usually in the terms and conditions. These can be muddy waters. Don’t be afraid to talk to an expert on how to navigate these threats. - Ransomware/Malware Ransomware
is like malware in that they are both criminal software used to take control of your computer and/or your information stored. Ransomware attacks are on the rise. Companies like DSA Technologies can help you build your line of defense through software against this type of attack. It’s estimated that an organization will fall victim to ransomware every 14 seconds in 2019. A single attack could leave you out of business for a week or more. Could you afford to be out of business that long? - IoT (Internet of Things) What I call “Internet of Threats”
IoT devices include internet enabled devices (i.e. iPhones, Amazon Alexa, Printers). There will be more than 20 billion IoT devices by 2020. How are the increasing amounts of data being secured? In most cases it’s not. There are manufacturers who have no security on their IoT devices, meaning anyone can access them. With so many devices being used, businesses should be aware of the security in place on IoT devices. Each device represents a different access point for attacks. With the rise of internet enabled devices the rise of attacks is inevitable. Ensure that your devices for your business are secure to protect sensitive data. - Single Factor Passwords
Single factor passwords are when you use a username and a passcode to log in. This is traditional and the method most websites maintain. Unfortunately, most passwords can be cracked in a matter of minutes. A second line of defense can help you and your business protect your data. An added defense line is the use of multi-step or two-step authentication passwords. This means that to log into your account, you can enter your password, but then a second step will require you to enter additional information, like a unique code sent to your cell phone. Having at least two steps make hacking your account more difficult in turn making your data less of an appealing target.
DSA Technologies’ resident Cyber Security Expert, Michael Reese is there to assist businesses tighten their security.
Visit DSA Technologies to learn more about how they can assist your business.